Kraków 2007-09-01
269 Section 1984-05-05
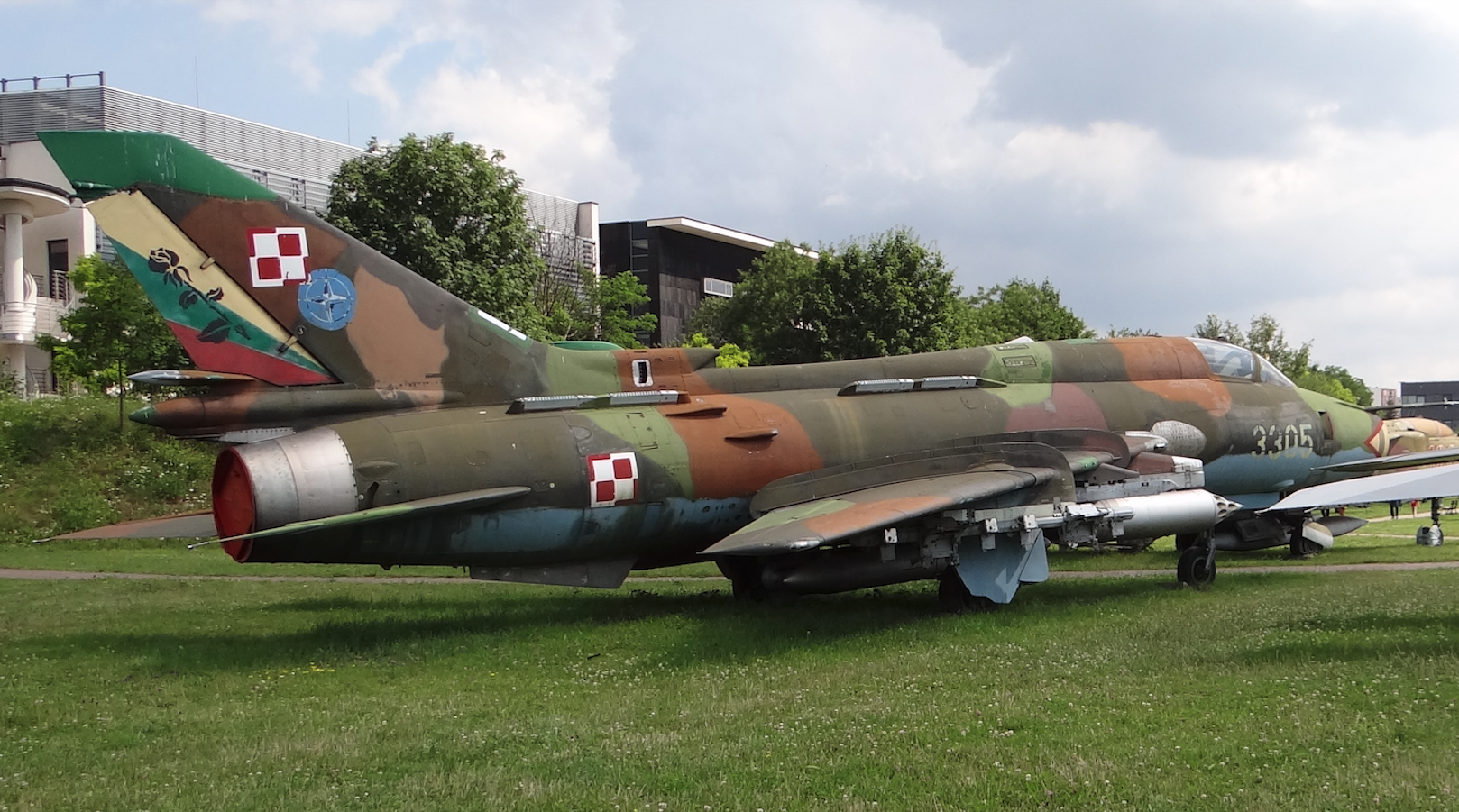
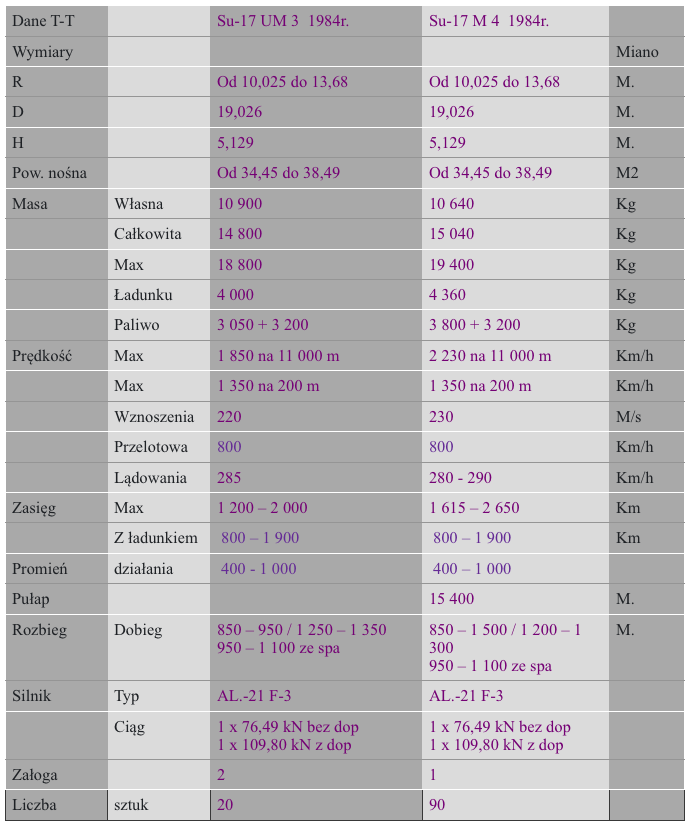
OKB Sukhoi Su-22 M 4 K, Su-22 UM 3 K. Poland.
Supersonic fighter-bomber aircraft with variable wing geometry.
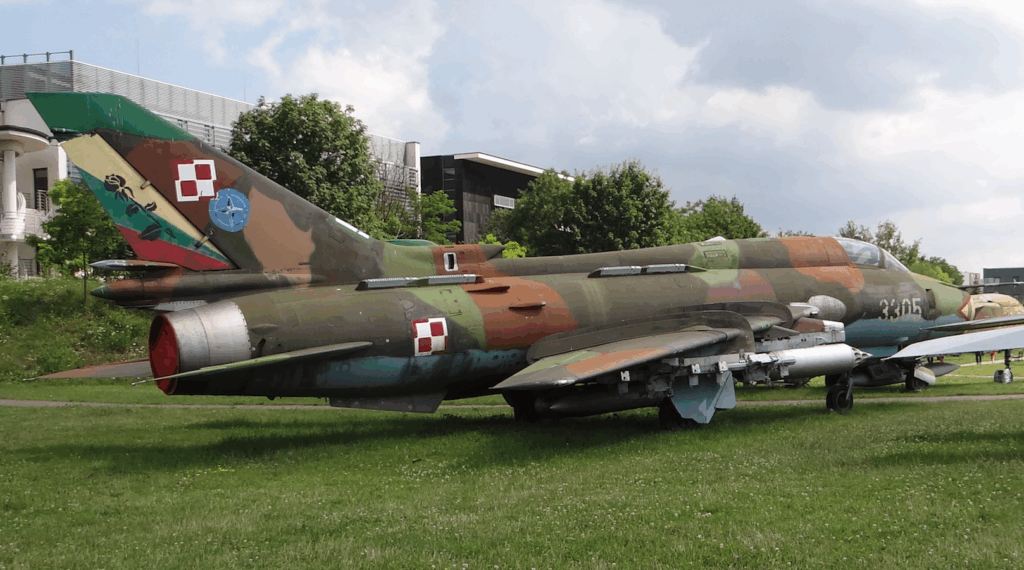

Sukhoi Su-22 M 4 K design.
Single-seat, single-engine fighter-bomber aircraft. Built in a classic layout with a wing with variable geometry. Medium-wing. The fuselage is made of aluminum and titanium alloys.
The wings consist of a fixed part and external movable parts, 4 m long, taking two positions. The minimum sweep angle is 30 degrees. The maximum is 63 degrees. This is also the sweep angle of the fixed part of the wings. Both parts are connected to each other by hinges. At the front, by means of a large bearing pin, which is the axis of rotation. At the rear, the support is a four-roller carriage moving on guides attached to the interior of the stationary part. The movement is carried out by a hydraulic system. The stationary parts are equipped with two sections of slotted flaps on the trailing edge. The outer parts have ailerons and slotted flaps on the trailing edge. Three-section gills (slots) are placed on the leading edge. The wing has two pairs of high aerodynamic guides and three pairs of smaller aerodynamic guides reinforcing the structure of the stationary parts of the wings. The wing covering was made by chemical etching. The control surfaces are made of 3-layer glued plates with honeycomb filler.
The fuselage has a semi-monocoque structure and a cross-section close to circular. The maximum diameter is 1.75 m, and the fuselage length is 15.572 m. Up to frame no. 13, the fuselage is tilted down by 3 feet. Technologically, it is divided into two parts. The division is at frame number 34. The removable rear part of the fuselage allows access to the engine. Frontal air intake with a central inlet cone that can take two positions. The pilot’s cabin is airtight and air-conditioned. It provides excellent working conditions and good visibility. The cabin is located between frames number 4 and 9. K-36 ejection seat class 0-0. It allows safe exit from the aircraft at speeds from 0 km/h to 1,300 km/h, at any altitude. The canopy opens upwards to the rear. A periscope for observation of the rear half-zone is placed on the fairing. Armored windshield. Four air brakes are placed in the rear part of the fuselage.
Horizontal plate stabilization with an angle of 55 degrees at 25% of the chord. Mounted with a negative lift of 3 degrees. Anti-flutter masses are mounted at the ends. The deflection ranges from +25 degrees 30 minutes to -10 degrees. Vertical stabilization with inflow, divided into rudder and stabilizer. The sweep is 55 degrees. The stabilization is supplemented by an under-fuselage steering wheel.
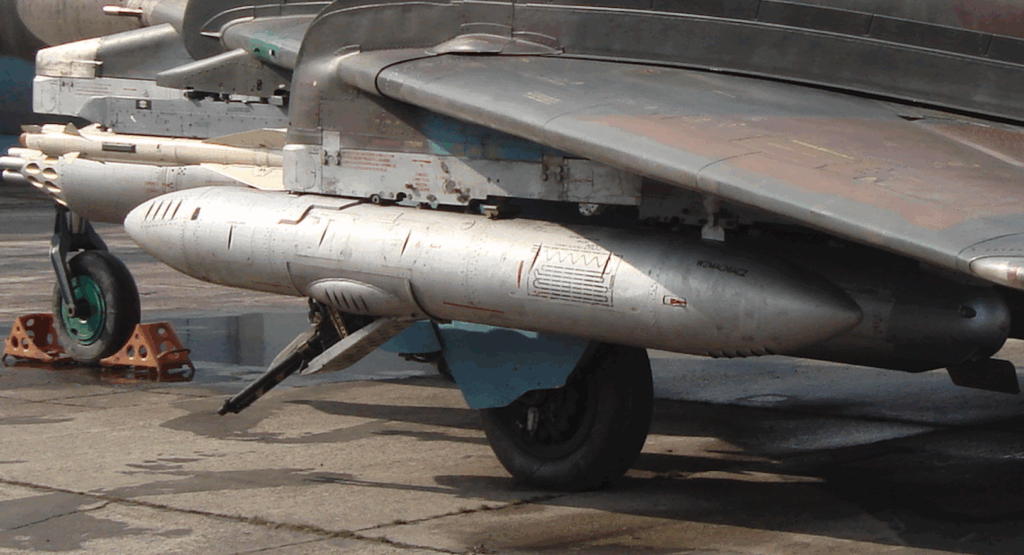
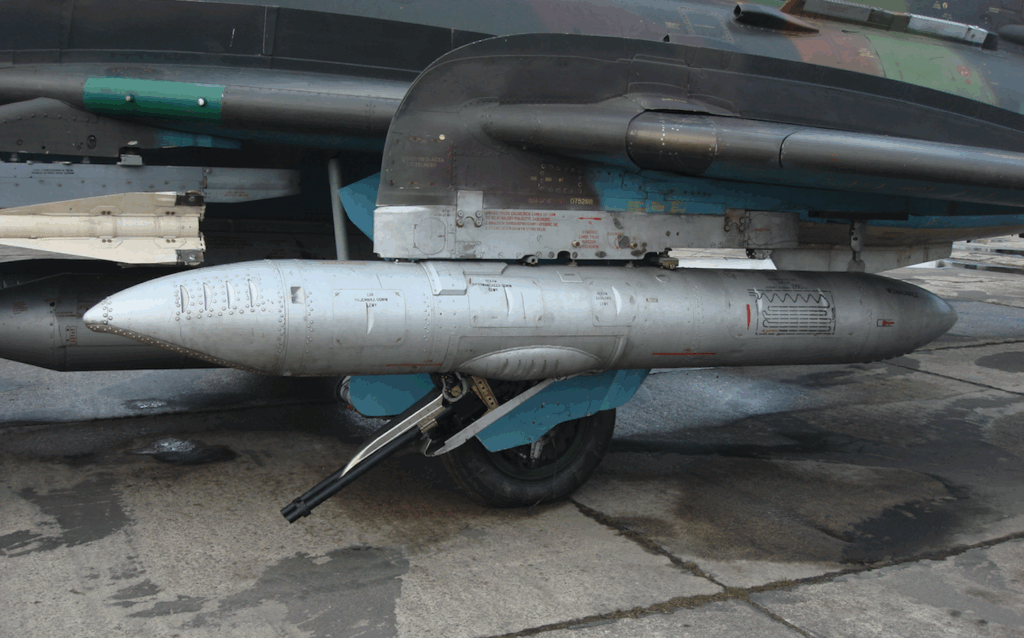
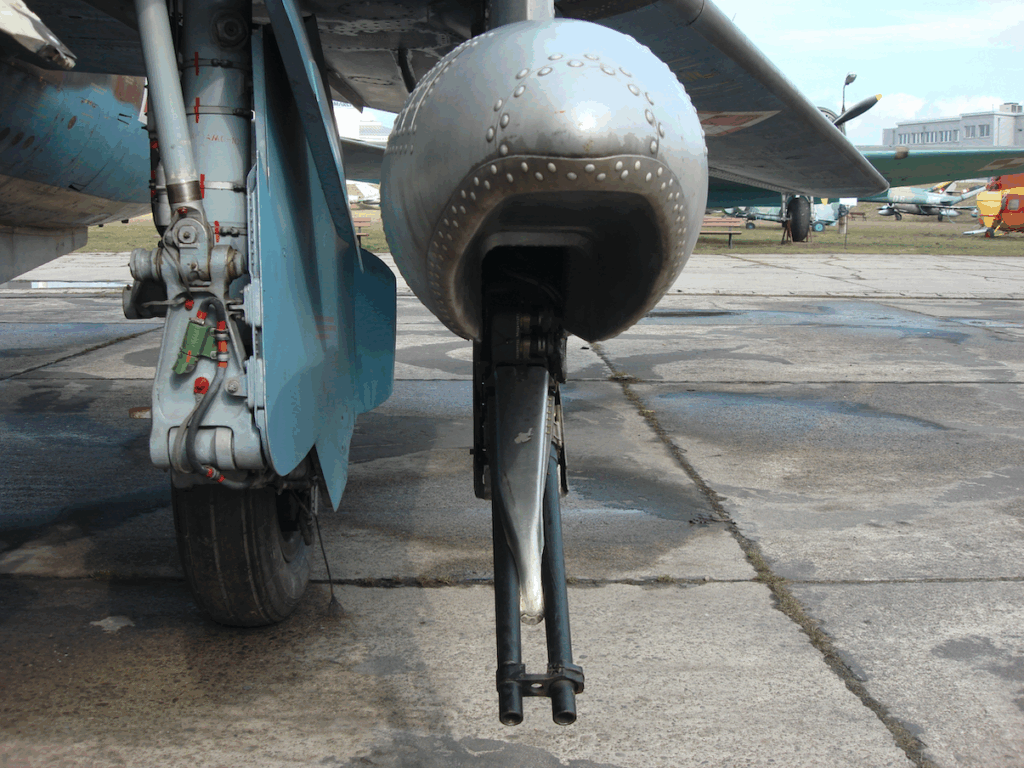
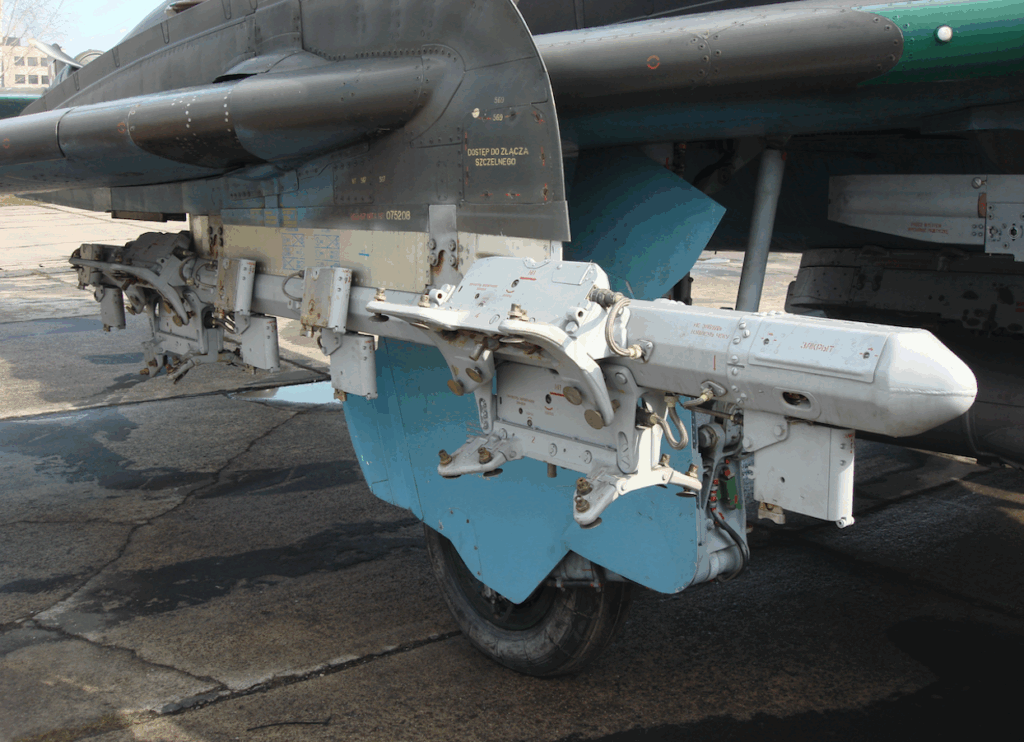
Three-support landing gear with oil-pneumatic shock absorbers and hydraulic brakes. Steerable front wheel, measuring 660 x 200 mm, pulled forward into the chamber under the cabin floor. Main landing gear also with single wheels, measuring 880 x 230 mm. The landing gear base is 5.24 m, the main landing gear spacing is 3.85 m.
The design of the Su-22 UM 3 K.
Differences from the single-seater version. The basic thing is the ability to perform training tasks with almost full combat capabilities of the single-seater version. The aircraft received a two-person cabin. The pilots’ seats were placed in tandem. A centralized ejection system with K-36 D S 2 seats was introduced. The instructor’s cabin was equipped with a periscope system, very similar to that used on Su-7 U aircraft. Space for the second cabin was created at the expense of reducing fuel tank no. 1. Overall, the fuel supply decreased to 3,050 kg, and thus the range. The equipment was modified by introducing the SAU-22 MU control system. The SPU-9 on-board intercom and MS-61 tape recorder were added. The left cannon was dismantled, but the weight of the aircraft increased to 10,900 kg. The armament capacity was reduced to 3,000 kg and therefore the second pair of under-fuselage nodes was abandoned.
Su-22 drive.
Depending on the customer’s wishes, Su-22 aircraft were equipped with AL-21 or R-29 engines. All Polish Su-22 aircraft were equipped with AL-21 engines, the same ones that powered Su-20 aircraft. These engines are being repaired in Warsaw, Poland.
AL-21 is the A. Lulka AL-21 F-3 engine with a thrust of 1 x 76.50 kN, and with afterburning 1 x 110.00 kN. This engine is specially adapted for flights at low altitudes. It is a single-flow turbine consisting of; a 14-stage axial compressor, an annular combustion chamber, a 2-stage turbine and an afterburner. The engine is cooled by air taken in by 4 grips placed on the fuselage in the rear part.
Fuel: T-1, TS-1, RT kerosene. IPM-10 oil or synthetic WNII-50. Specific fuel consumption 0.9 – 1.2 kg/daN/h, with afterburning 1.5 – 2.0 kg/daN/h. Engine service life is 900 – 1500 hours depending on the production series. Inter-overhaul period 350 – 450 hours.
The fuel system consists of 4 tanks located in the fuselage and two integral ones located in the moving parts of the wings. Additionally, the aircraft can carry 4 additional tanks (2 under the fuselage and 2 under the wings).
Equipment of the Su-17 M 3.
Automatic control system SAU-22 M 1. Navigation complex KN-23 including; inertial system IKW-8, navigation radar DISS-7, aerodynamic data center SWS-P-72, data input panel and W-144 calculator. Short-range navigation system RSBN-6 S. Laser rangefinder Fon-1400. RW-15 radio altimeter. ASP-17 B dual-function sight. SPO-15 ŁS warning station. WRe. SPS-141 MWG Gvozdika active jamming station in the container. KDS-23 dipole and thermal flare launcher.
Su-17 M 4. Equipment
Navigation system coupled with the targeting system into a single PRNK-54 navigation and targeting system (pricelno-navigation complex) with an Orbita-20-22 on-board computer. Before the flight, the coordinates of the target and turning points on the route are entered into the computer. The system allows for an attack in “all weather conditions”. Automatic control system SAU-22 M 1. Long-range navigation system RSDN-10 (radiotechnicheskaya system for long-range navigation), which its predecessor did not have. VHF radio station R-862. Radio altimeter RW-4 or newer RW-21 – Klen-54. ARK-15 M or newer ARK-22. Laser rangefinder Fon-1400. The weapon system includes an ASP-17 B or newer optical sight. Automatic system for avoiding obstacles in low-altitude flight. Automatic control system SAU-23 B. The machine can be controlled automatically or manually by the pilot. Inertial course and vertical system IKW. Doppler speed and drift angle meter DISS-7. Active and passive jamming systems. System warning about enemy radar station radiation and anti-aircraft missile launch enabling automatic execution of anti-missile maneuver. Friend-foe identification system. Devices; SRO-2, SPO-10, MRP-66. Head-up display on the windshield (HUD).
Su-22 M 4 K armament.
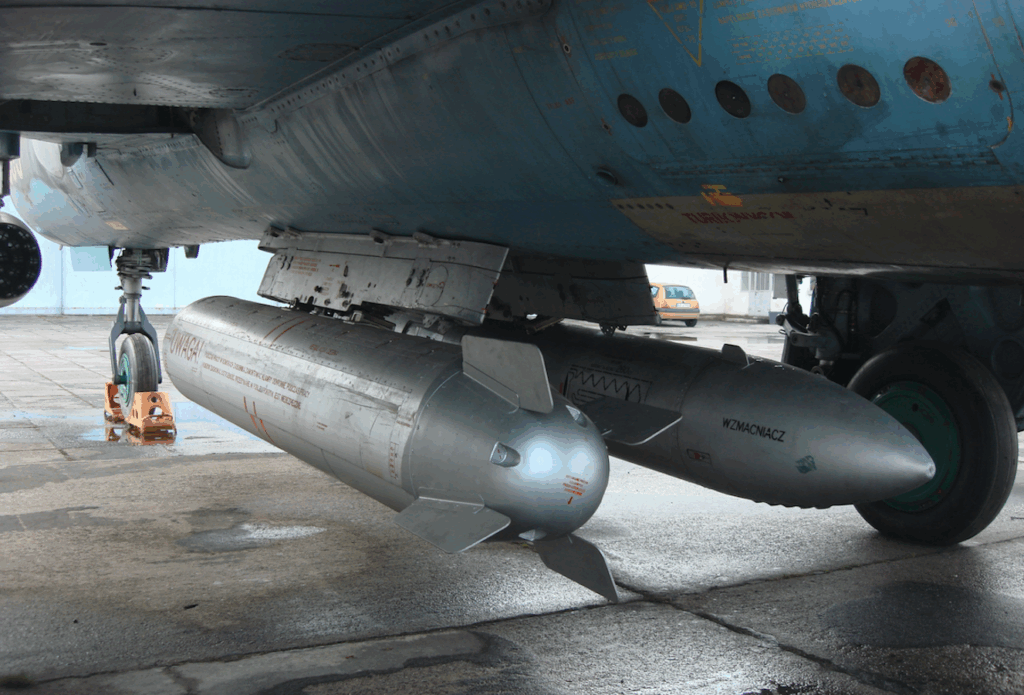
Weapon weight is 4,000 kg. The aircraft has 10 knots. 4 under the fuselage, 4 under the wings + 2 under the wings for the R-60, R-55 or R-13 class of p-p kpr. The fixed armament consists of two NR-30 cannons, 30 mm caliber, designed by A. Nudelman and A. Richter, with a supply of 160 rounds of ammunition each. Weight 66 kg, rate of fire 900 shots/min, projectile weight 410 g, and initial velocity 780 m/s. They are placed in the wing bases.
SPPU-22-01 (KU-22K) gun pod controlled by a computer, with a total weight of 290 kg. In the front it contains a double-barreled GSz-23 cannon placed on a movable carriage, thanks to which it can be tilted down by an angle of 23 degrees. In the back there is a control system and 260 rounds. The entire pod can be suspended with the barrels forward or backward. Data must be entered into the computer before the flight – speed and flight altitude.
Another gun pod used is the UPK-23-250 also with a GSz-23 cannon, but stationary. Empty weight 78 kg, and after loading 250 rounds it is 217 kg. Length 3.166 m, diameter 340 mm.
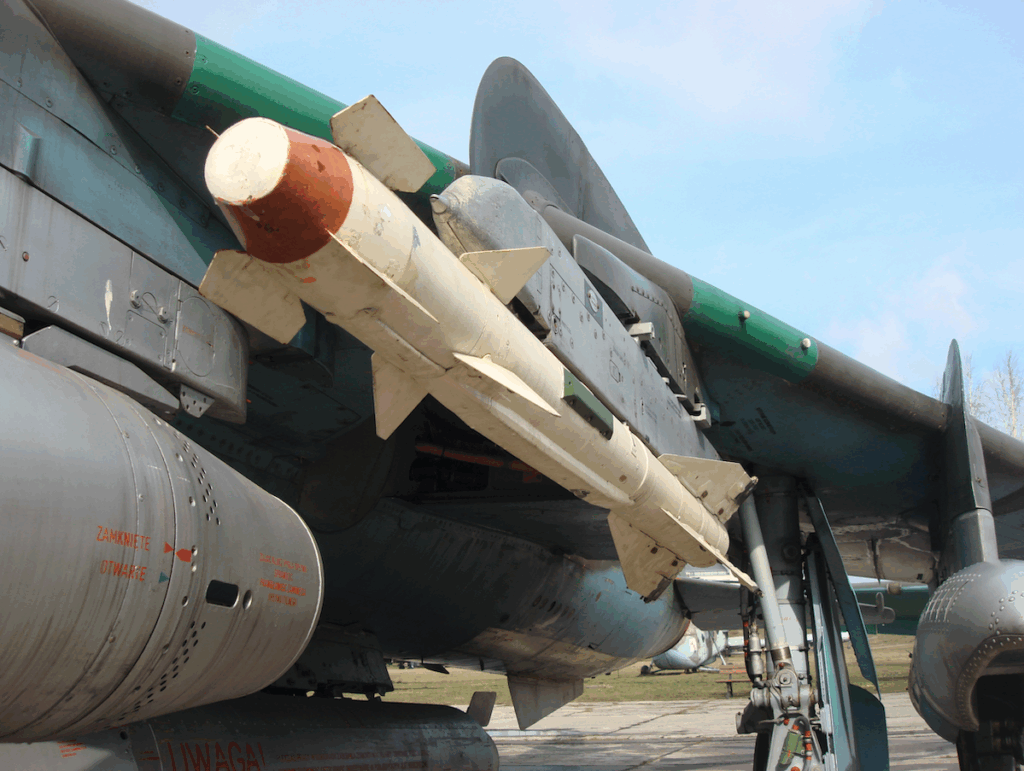
Guided missiles of the anti-aircraft class; R-60 – has a mass of 45 kg, length of 2.10 m, caliber of 0.12 m. The missile hits targets at a distance of 200 to 7,200 m.
Guided missiles of the anti-aircraft class; K.p.r. H-25 of modular design. It is a commonly used missile of MiG-27, Su-17, Su-24 and Su-25 aircraft. It has a replaceable warhead; radar-guided – H-25 MR (izdielienie 715), laser – H-25 ML (izdielienie 713) or anti-radiation – H-25 MP (izdielienie 711). Depending on the version, it has a mass of 300 – 320 kg. The mass of the warhead is 90 kg. The missiles fly at a speed of 850 – 900 m/s. Length is 4.353 m, caliber 0.275 m.
K.p.r. – H-29 L (izzielienie 64) laser-guided. It is the heaviest missile carried by an aircraft. Weight 657 kg, including 317 kg warhead. Range 8 – 10 km. Dimensions; length 3.875 m, wingspan 0.78 m, caliber 0.38 m. It is used to combat heavily armored targets.
Guided missile H-58 – anti-radiation. K.p.r. of the older generation – H-23 and H-28.
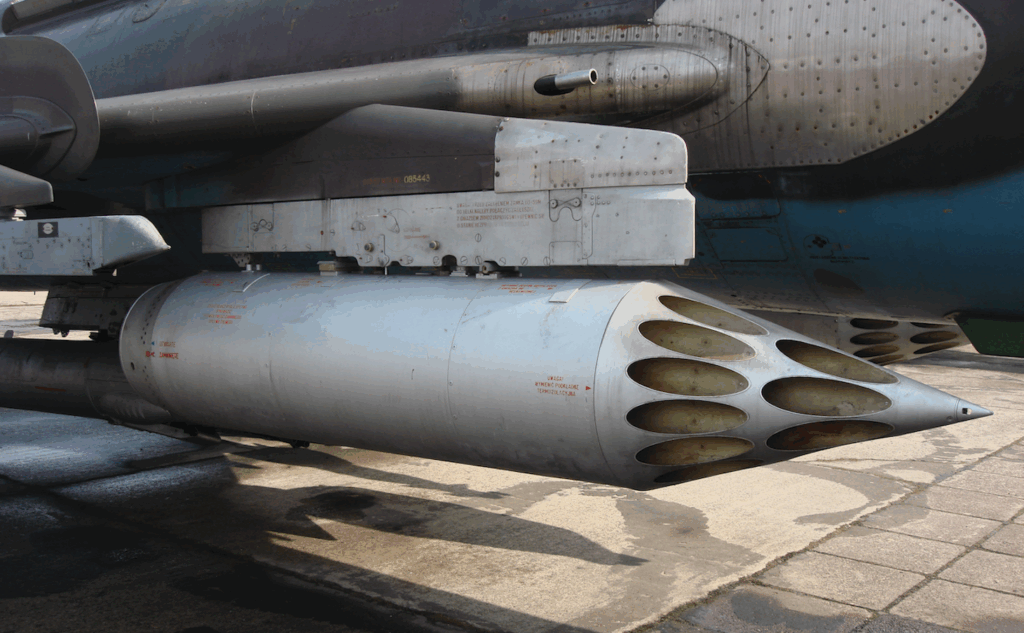
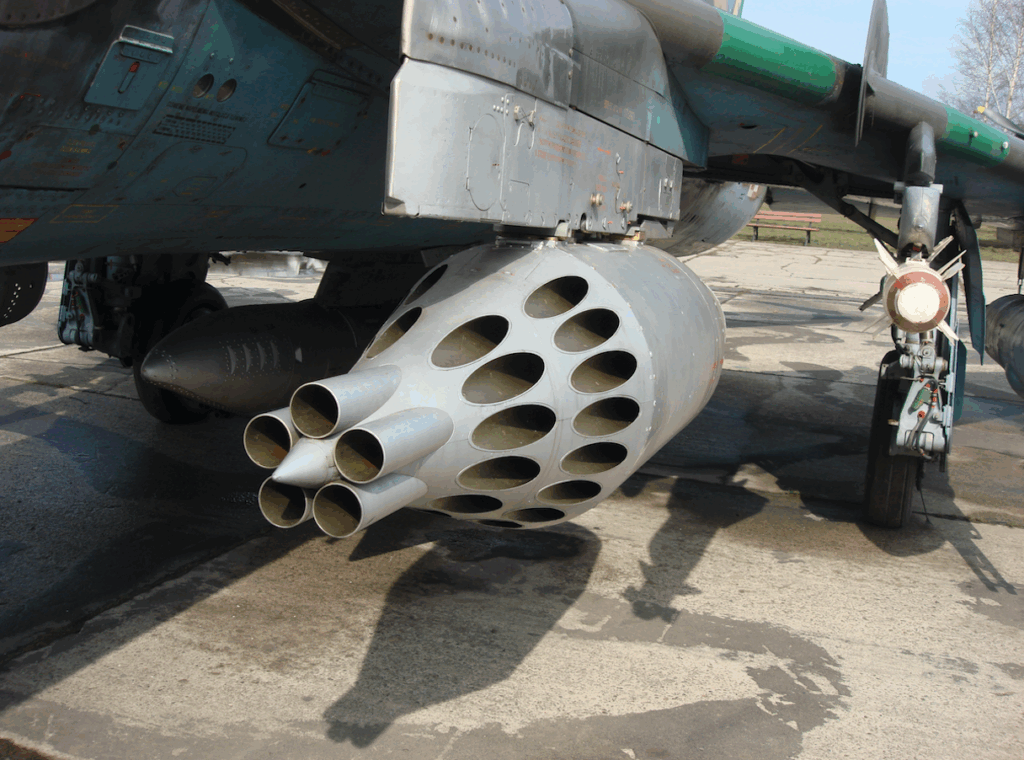
Unguided rocket missiles of caliber from 57 to 370 mm; S-5 57 mm caliber, launched from a UB-32 container. S-24 is a heavy rocket missile designed to destroy bunkers, bridges, armored trains, etc. S-8 80 mm caliber, launched from a B-8 M 1 container with 20 pieces. Missile weight 11.65 kg, warhead 3.6 kg, length 1.445 mm. In the anti-tank version the S-8 KO penetrates armor 420 mm thick. S-13 122 mm caliber, launched from a B-13 container with 5 pieces. The missile comes in two versions; anti-tank S-13 T, weight 67 kg, penetrates 1,000 m thick armor and S-13 OF, weight 68 kg, at the moment of explosion 1,800 fragments are created. S-25 overcaliber 370 mm. It comes in several versions. In Poland, the fragmentation-explosive version S-25 OF, weight 480 kg, warhead 190 kg, length 3.31 m, caliber 340 mm. The projectile hits an area of 1,820 square meters.
Free-fall and guided bombs; FAB-500 L – weight 500 kg, laser-guided. FAB-500 M-62 – developed in 1962, length 2.43 m, caliber 400 mm, the bomb hits an area of 1,500 square meters. ODAB-500 P fuel-air bomb. OFAB-250-270. OFAB-100-120. Cluster bombs weighing 1-2.5 kg; AO-1 SCz, AO-2.5 RT (fragmentation), ZAB-2.5 (incendiary), PTAB-2.5 (armor-piercing). Placed in cassettes; RBK-250, RBK-500, KMGU (length 3.70 m, diameter 460 mm, weight 525 kg).
Polish bomb cassettes produced in “Dezamet” in Nowa Dęba; ZK-300 Kisajno (cluster container), length 3.40 m, diameter 450 mm, weight 465 kg, including 252 kg of 315 LBOk-1 ball bombs. The cassette consists of three sections. After dropping, it flies freely for a distance of up to 3 km. After a set time, it detonates; the front section at an angle of 30 degrees to the left, the middle section horizontally to the left and right, the rear section at an angle of 30 degrees to the right. The bombs fly out in packages of 3-4 pieces. After free flight, they are launched from each other. The LBOk-1 bomb is 67 mm in diameter, weighing 0.8 kg, including 0.16 of the charge, and inside there are one-gram balls with a diameter of 6.35 mm. The radius of destruction is 40 m. ZR-8 (pipe container). It has 8 packages with ball bombs launched backwards. There are also versions ZR-2 and ZR-4.








Written by Karol Placha Hetman

