Kraków 2007-09-05
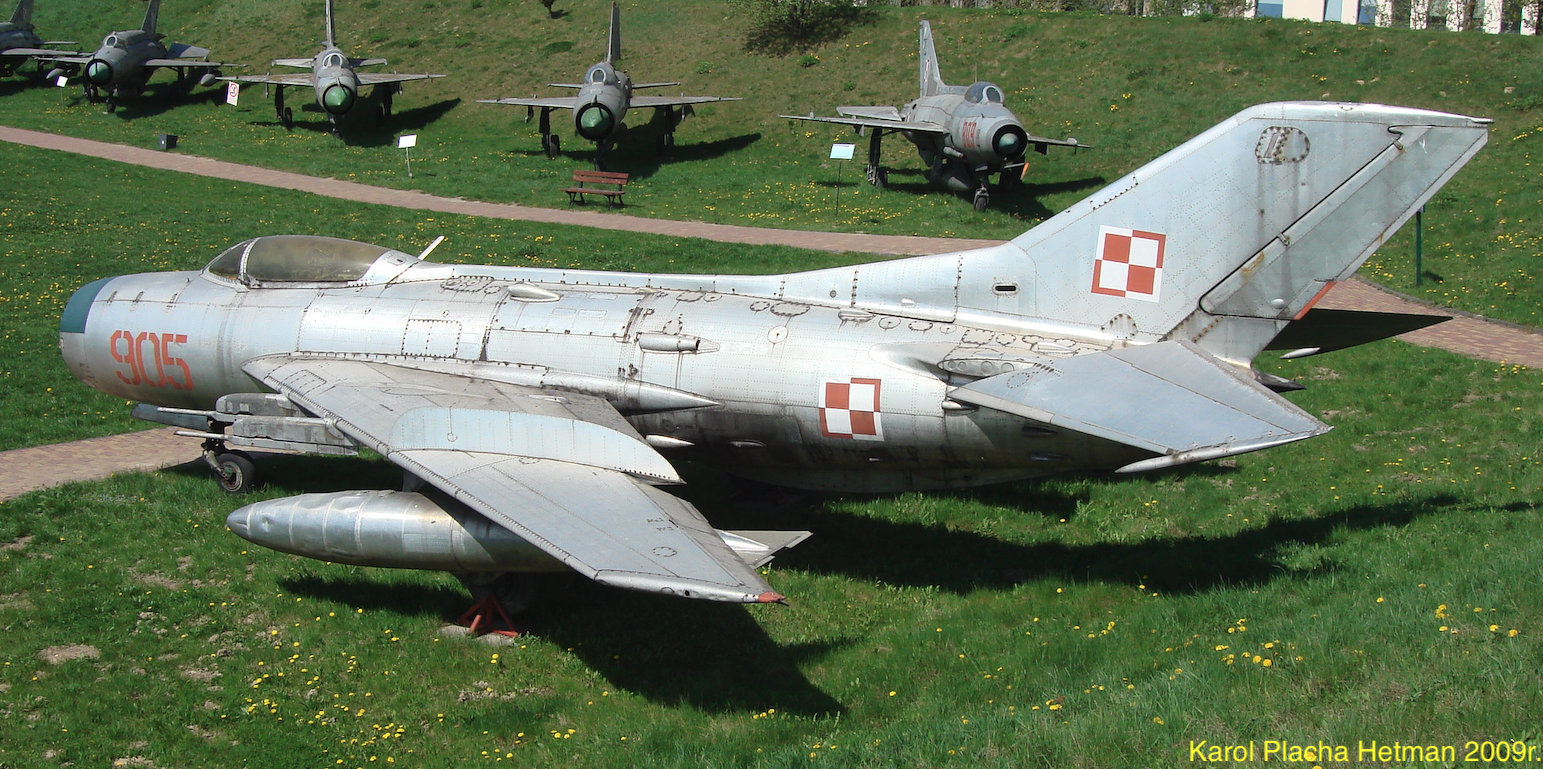
OKB Mikojan and Guriewicz MiG-19 P, PM.
The design of the MiG-19 P, PM.
The MiG-19 is a single-seat, twin-engine supersonic fighter, mid-wing, all-metal. Equipped with SR (radar station, radar). The airplane is capable of flying at supersonic speed.
MiG-19 wings.
A 55 degree bevel (to the 1/4 chord line), 8% relative thickness at the ends to 8.74% at the hull. Negative ascent -4.5 degrees, span 9 meters, bearing area 25.0 square meters, elongation 3.24. Half-shell wing structure, typical for OKB MiG office planes, with main, auxiliary, front and rear spar and 27 ribs. Cover of duralumin wings with a thickness of 1.5-2.0 mm. The passage between the fuselage and the wings is profiled. On the upper surface of each wing, an aerodynamic crest 32 cm high. Ailerons 0.78 m2 each, with internal aerodynamic compensation. The left aileron is equipped with a trimmer. Aileron deflection range 20 degrees, trimmer 15 degrees. In order to increase the effectiveness of the lateral control of the plane at high speeds, kinematic interrupters coupled with the ailerons were installed on the lower surface of the wings (when the aileron is deflected down, the corresponding interrupter on the opposite wing extends). Flaps, as in previous planes, with a sliding axis of rotation (about 40% of the chord to the rear). Flap area 2 x 1.72 square meters, take-off angle 15 degrees and landing angle 25 degrees.
Under the wings there are 4 launchers for the RS-2US p-p class guided missiles, which are the distinguishing feature of the PM version.
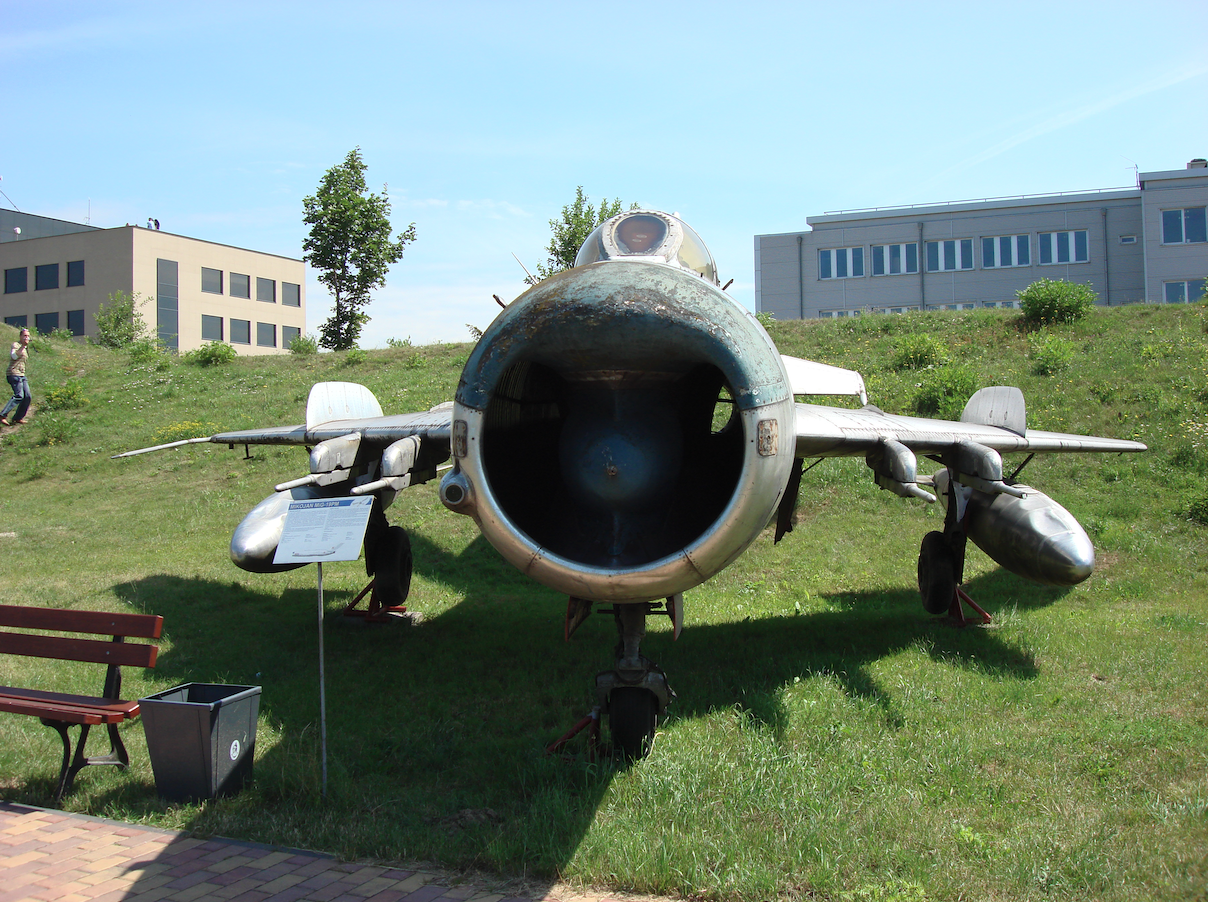
The fuselage of the MiG-19 aircraft.
The structure of the MiG-19 fuselage is semi-shell, circular cross-section flattening towards the end. It is divided into a front and a rear part, separated between frames 20 and 20A. In the front, the air inlet is separated by a vertical partition, above it the AKS-3M or AKS-5 photo rifle, at the bottom there is the base of the PWD-4 air pressure receiver. At the top, between the 1st and 4th frames, a compartment with a battery and radio equipment. Front landing gear retracted between frames 1 and 5A. Pilot’s cabin between frames 4 and 9 (the cover extends to frames 13). At the bottom, between the 11th and 14th frames, an air brake with an area of 0.45 m2 and a deflection angle of 45 degrees. Two other airbrakes (total area 1.04 m2, 25 degree deflection) on the sides of the fuselage between frames 22A. and 26. Frame 15 starts the engine compartment, and frame 21. is an under-hull aerodynamic comb with a cushioned tail bumper. A profiled fairing at the end of the fuselage. In the bottom of the rear part of the fuselage a recess with a TP-19 braking parachute, 4.5 m in diameter. Working hull covering, duralumin, 0.6-1.2 mm thick. Additional steel inner coating near the engines.
In the P and PM versions, the fuselage has been lengthened by 0.90 m. The front has a radar with two separate antennas: search and tracking. Front cannon removed.
Pilot’s cabin, semi-hermetic, ventilation type, protected by armor plates (front 10 mm, rear 16 mm, behind the pilot’s head 25 mm). The headrest also serves to break the closed cockpit cover in the event of the pilot’s ejection. Two-part canopy: a fixed part with a 64 mm multi-layer windshield and a movable part that can be moved to the rear. Ejection seat with face curtain, powder charge fired with telescopic mechanism (for safer ejection of the chair at high airspeed). KKO-1 oxygen device. In order to prevent dust, water or snow from entering the cabin during standstill, it can be hermetically sealed from the outside. Fuselage length 10.428 m, plane without Pitot tube 12.54 m, total – 14.64 m.
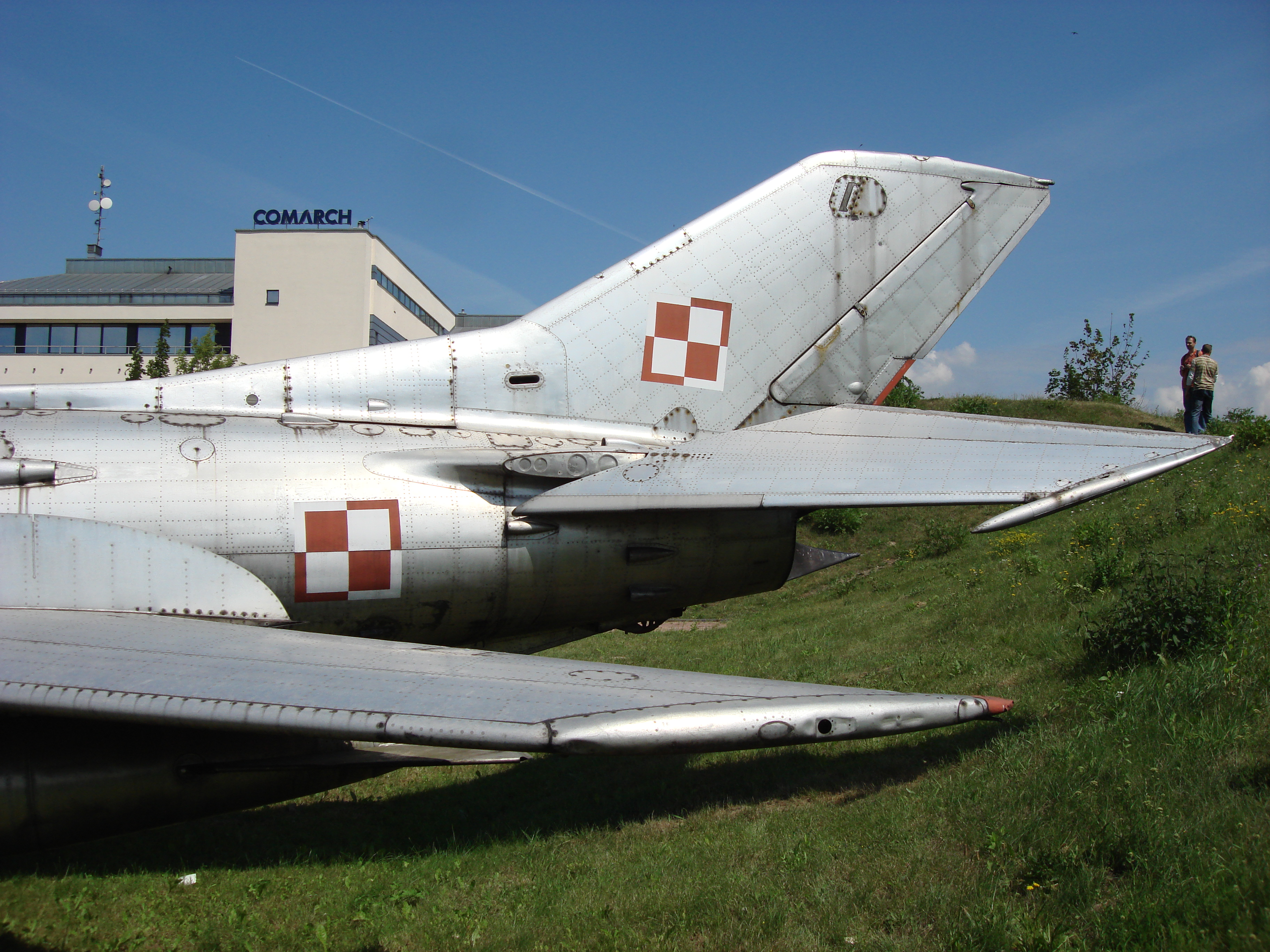
The tail of the MiG-19 plane.
Vertical tail. Leading edge skew 57 degrees 37 minutes (there is a greater skew at the fuselage), relative thickness 8%. The area of 4.17 m2, including 0.93 m2 is occupied by a rudder tilted by a 25 degree angle. On the left side of the vertical tail, an automatic rocket launcher was mounted, with four signal rockets of different colors: yellow, green, red and white.
Plate height fix, with a movable part area of 5.5 m2 (total 7.78 m2) and deflection angles of 17 degrees downwards and 7 degrees 10 minutes up (measured in the plane of the air stream). Relative thickness 7%, angle of skew 55 degrees, span 4.46 m. In the tail control system there is a BU-14MS non-return amplifier and an ARU-2A automatic unit that adjusts the loads on the control stick to the pilot’s habits. Control system powered by a separate hydraulic system, duplicated by the main hydraulic system; additionally, as a second protection – the APS-4 electric mechanism.
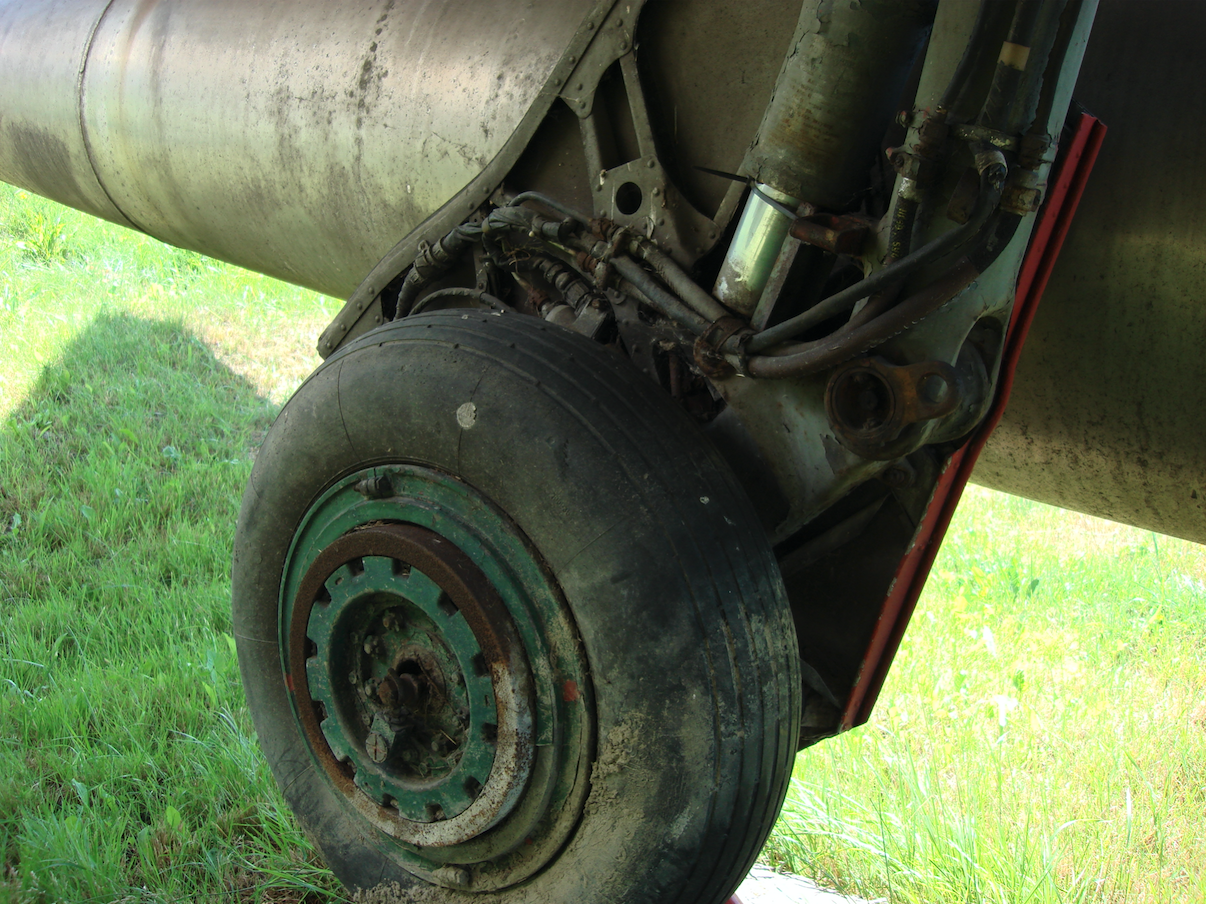
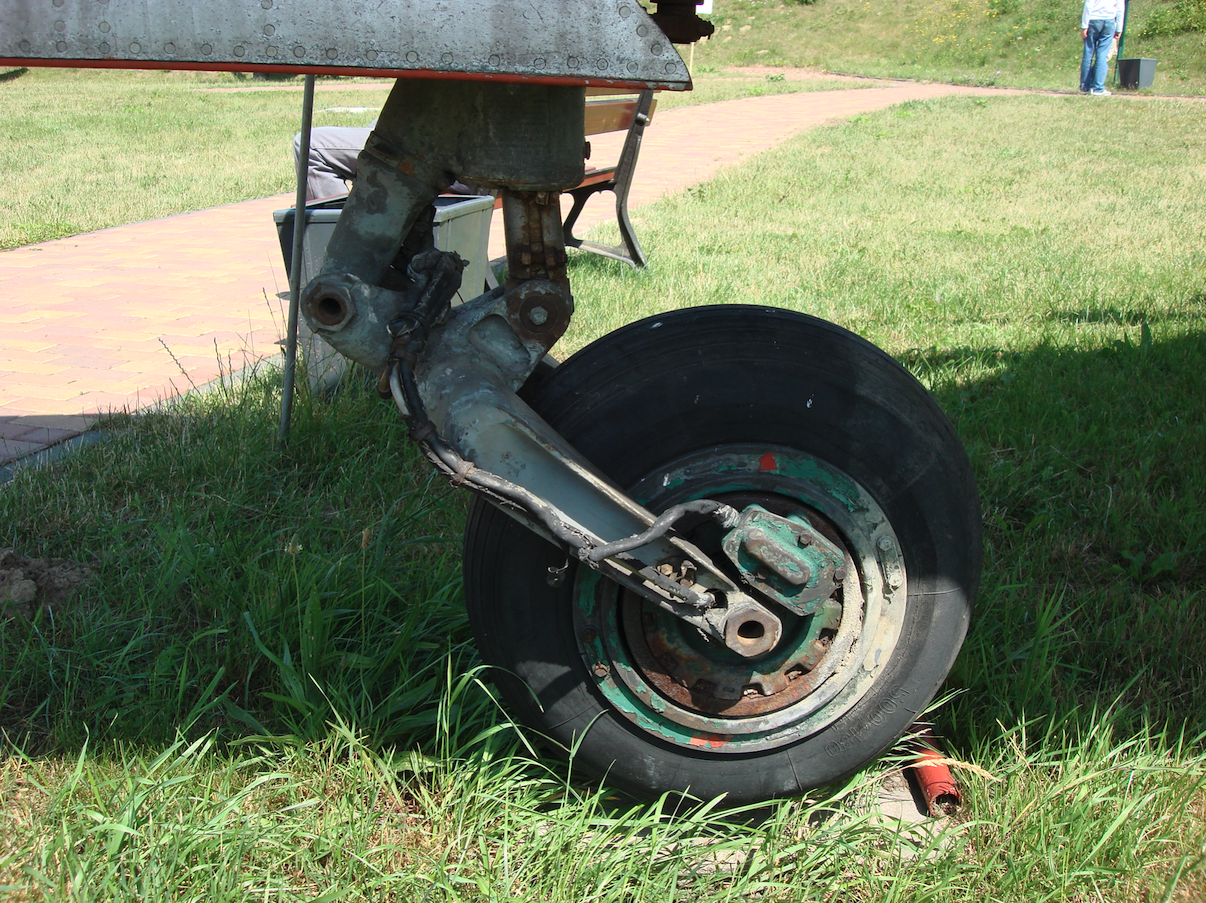
The landing gear of the MiG-19 aircraft.
The structure of the aircraft landing gear is similar to that of the MiG-15 and MiG-17 aircraft. The undercarriage is three-support, rocker type, oil-air shock absorption, the main undercarriage is retracted into the wings, the front into the fuselage towards the front. Wheel dimensions: 500 x 180 mm, main 660 x 200 mm. Main landing gear track 4.156 m, chassis base 4.448 m.
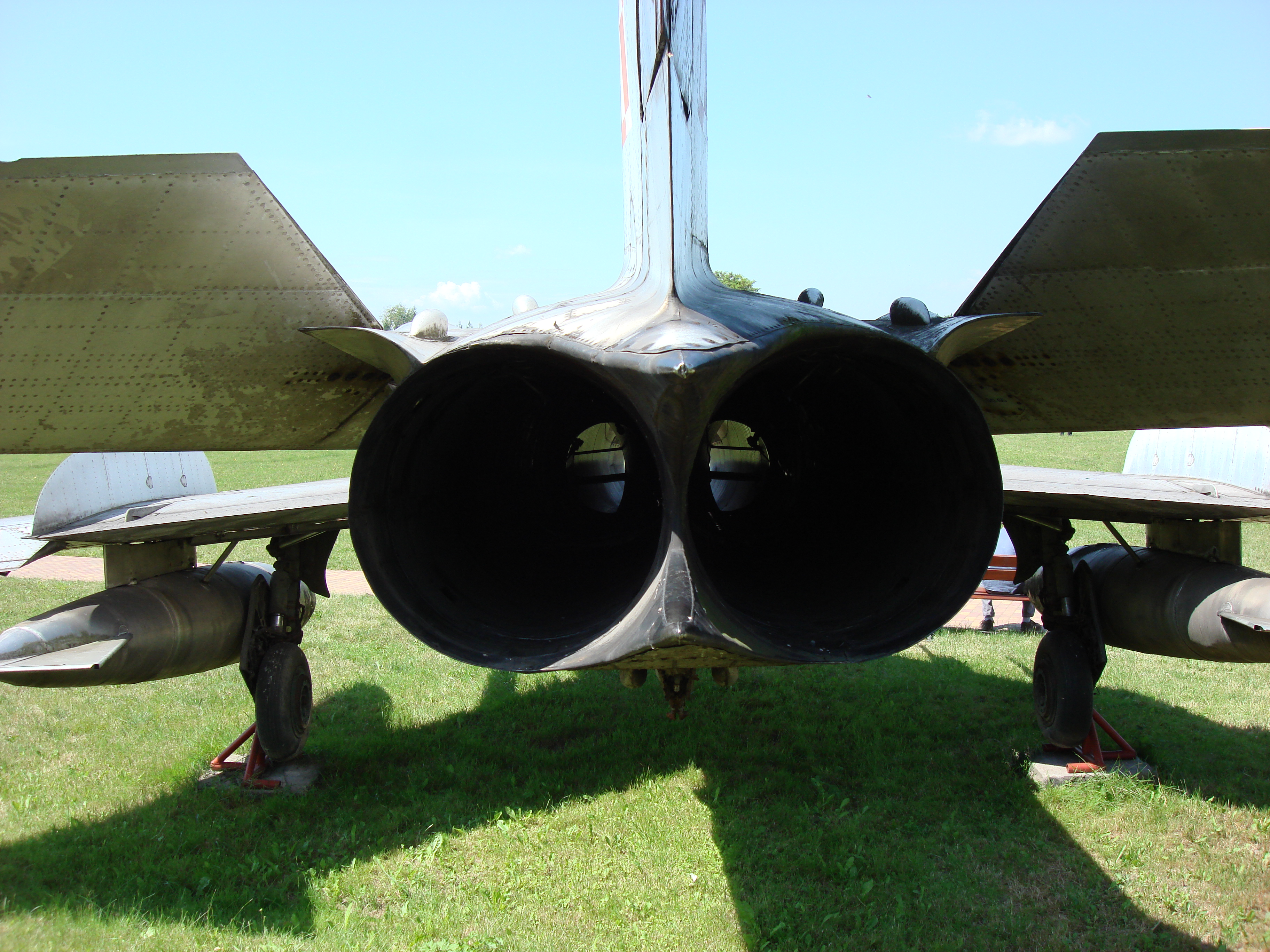
MiG-19 engines.
The power unit consists of RD-9 B engines designed by S. Tumański with a thrust of 2 x 2,550 kG, and with afterburning – 2 x 3 237 kG. The engine consists of a 10-stage axial compressor, with a 5-stage anti-pumping bleed, 10 glow tubes, 2-stage turbine, afterburner, three stages of nozzle adjustment. Four flexible fuel tanks with a total capacity of 2,155 liters. Additionally, two suspended fuel tanks with a total capacity of 1,520 liters.
MiG-19 PM plane: Two RD-9 B turbojet engines with nine-stage axial compressor and two-stage turbine. Fuel in a total amount of 2,170 dm3 in 4 hull tanks: two soft tanks behind the cabin (1,485 and 330 dm3) and two metal tanks under the engine nozzles (180 and 175 dm3). In addition, under the wings, on the BD-3-56 universal locks, it is possible to suspend two additional tanks of 760 dm3 or 400 dm3 (from MiG-17). Take-off thrust of the RD-9B engine at the maximum range (11 150 rpm) 2 x 25.5 kN, with afterburning – 2 x 32.4 kN. The activation of the afterburner is accompanied by an increase in specific fuel consumption by about 50-60%. This consumption is, for example, at a speed of 1000 km / h and a flight altitude of 11000 m, it is 0.12 kg / (N / h) in the maximum range and 0.18 kg / (N / h) with the afterburner on.
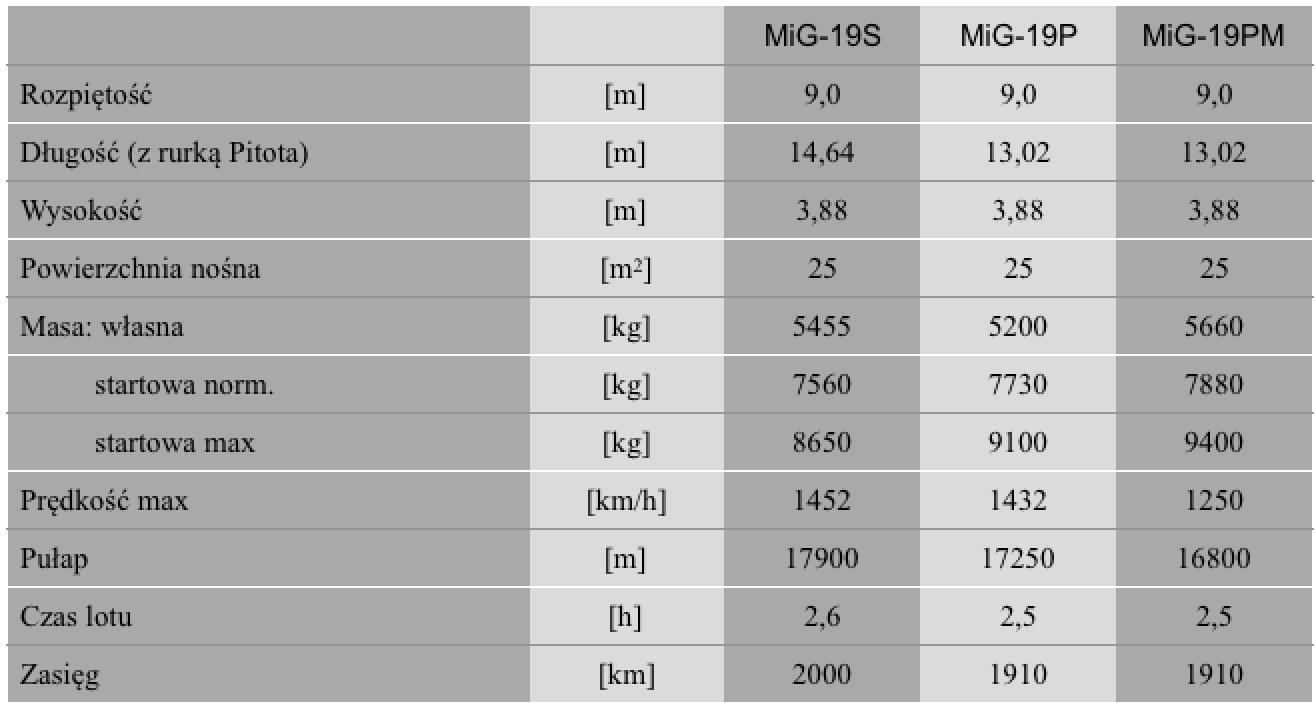
Data T-T MiG-19:
Written by Karol Placha Hetman