Turbo-shaft engines for helicopters
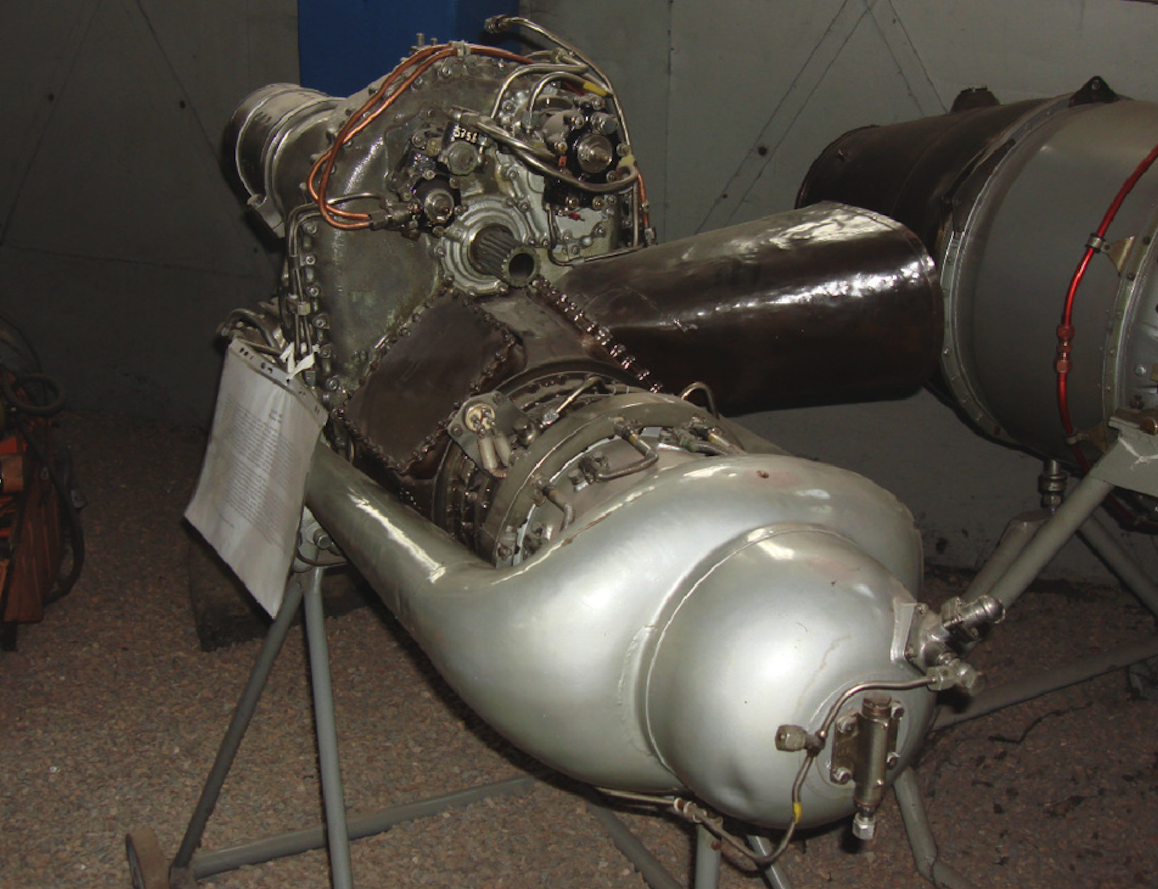
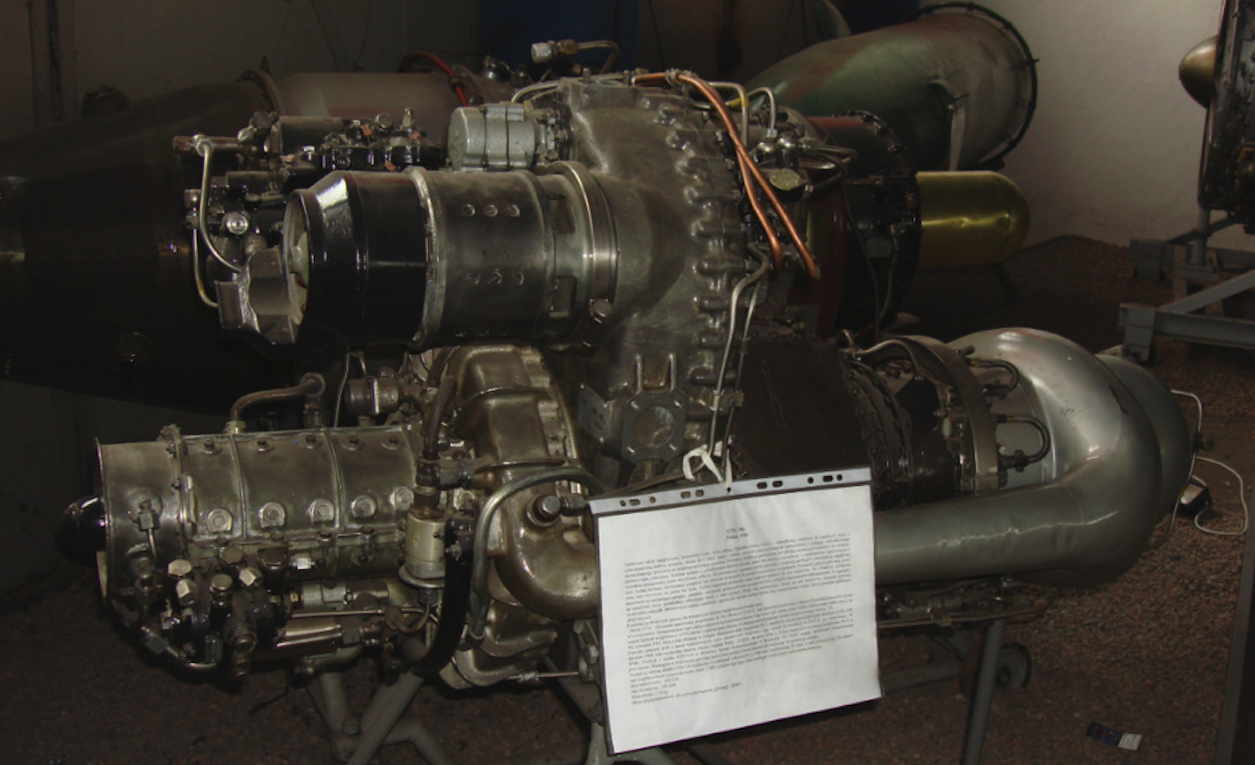
PZL GTD-350 engine. 1961 year.
The Soviet Mi-1 and Mi-4 helicopters were powered by piston engines. Turbine engines have already been widely introduced in the West. The Russians managed to obtain the Allison 250 engine. On its basis, Sergei Isotov’s team developed their own engine, which was designated GTD-350. The first engine start took place in 1961. The engine in a set of two copies was used in the Mi-2 helicopter. As the CCCP processing capacity was insufficient, an agreement was concluded in 1966 for the license production of GTD-350 engines at the PZL WSK Rzeszów plant. It was all the more purposeful as the entire production of Mi-2 helicopters was located in PZL Świdnik. In Poland, over 10,000 GTD-350 engines were built, and less than 1,000 were built at the CCCP.
The first versions of the GTD-350 engine had an inter-maintenance service of only 200 hours. At that time, the service life of the Mi-2 helicopter was 1,000 hours. Engineers from PZL WSK Rzeszów introduced many important modifications to extend the engine service life. The service life has been extended to 1,000 hours.
PZL GTD-350 engine data: dimensions, length 1.35 m, width 0.52 m, height 0.68 m, weight 135 kg. The engine has a power of 294 kW. The engine consists of a 7-stage axial compressor and one radial (centrifugal) stage. Two air passages lead compressed air to a single canned combustion chamber located at the rear of the engine. The combustion chamber is partially reverse flow. Fuel is supplied to the combustion chamber through two injectors; one centrally located working one and one slightly to the side spark plug, integrated with the spark plug. The compressor is driven by a single turbine. Another slow 2-stage turbine drives the main gearbox. The engine has four exhaust vents, two for the left and right side. But only two holes are used. If the motor is mounted on the left side, the right side outlets are plugged and vice versa. The take-off power is 313 kW (425 HP), the nominal power is 235 kW (329 HP). The speed of the compressor is 45,000 rpm. The rotational speed of the drive turbine is 24,000 rpm. The rotational speed of the output from the engine is 5,904 rpm. The fuel consumption at take-off is 0.496 kg / kWh. Electric motor starting with a current-starter.
Written by Karol Placha Hetman